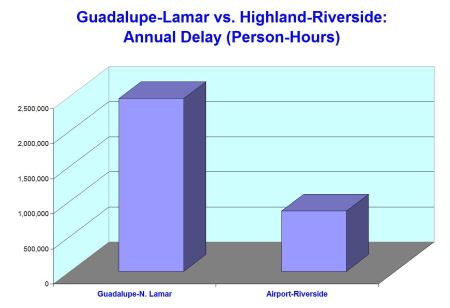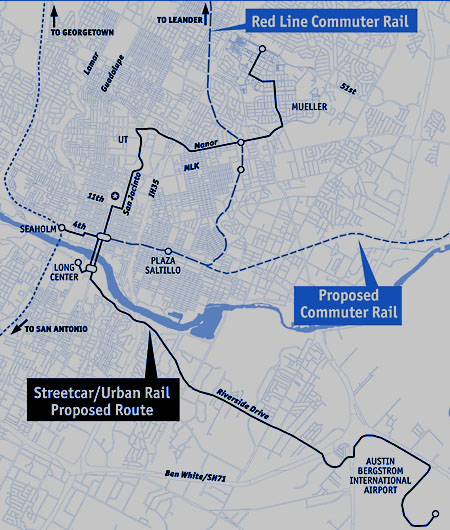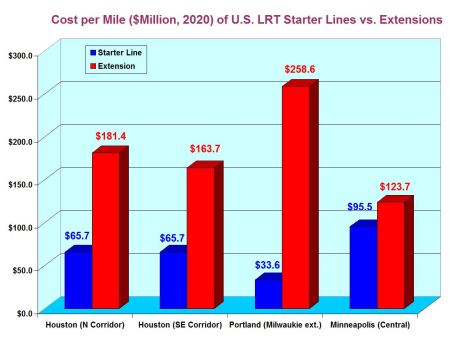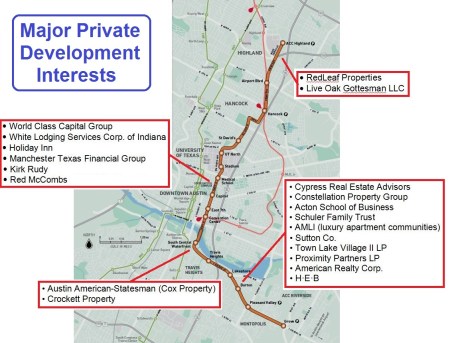
Map of urban rail line proposed for bond funding in November shows major private development interests and property owners that stand to benefit from selected route. Graphic: ARN. (Click to enlarge.)
♦
For years, the Light Rail Now Project, public transport advocates such as Dave Dobbs, Lyndon Henry, and Andrew Clements, and researchers and journalists such as Roger Baker have been criticizing Austin’s official urban rail planning process. In particular, they’ve been calling attention to the distortion of planning to avoid addressing bona fide mobility needs and instead defer to the needs and interests of real estate development.
In his analysis Connecting some dots on Austin’s urban rail planning, Baker revealed how planning for urban electric light rail was shifted away from a focus on crucial travel patterns in the heart of the city, and remade to promote development goals in more peripheral areas: “The dots in this case were partly the political momentum behind a new hospital district, combined with a new Opportunity Austin/Chamber-of-Commerce-recommended Austin growth policy.” Thus, “… in 2008, a city consultant, ROMA, recommended that the proposed light rail corridor be moved east to the San Jacinto Corridor (ultimately connecting several years later to the Red River corridor), as opposed to the previously-assumed Lamar Corridor alignment.”
Similarly, in their commentary Project Connect’s urban rail plan is “worse than nothing”, Dobbs and Henry explain how the official urban rail plan ignores the travel problems of the city’s core Lamar-Guadalupe axis in preference for catering to real estate and economic development development objectives. Now on the November ballot to seek voter authorization for General Obligation bonds to fund a 9.5-mile, $1.4 billion line strangely wandering from East Riverside Drive over a series of disparate, otherwise disconnected roadways to the former Highland Mall site, the proposed project, they say, is “primarily aimed at bolstering development plans and centered on the interests of private developers and the East Campus expansion appetites of the University of Texas administration.”
Rail transit and economic development
There’s certainly nothing wrong with efforts to site or cluster new development around or near rail transit stations. On the contrary, transit agencies, modern planning policy, and the transit industry all encourage and seek such development, often in the form of transit-oriented development (TOD) or transit-adjacent development – typically, synergistic residential development and activity center patterns that promote transit ridership, reduce dependency on personal motor vehicles, and help minimize urban-area sprawl.
But as the current controversy illustrates, a huge problem arises when rail planning forsakes serious mobility needs in deference to a predominant quest by political officials and civic leaders for obsessively desired real estate and economic development. Neglecting mobility function in favor of embellishing or promoting real estate development not only is a disservice to overall community needs, but also can be harmful to cost-effectiveness and other critical performance characteristics of good rail transit. Furthermore, rail transit can be a magnet for development, but this happens more or less in direct correlation with mobility effectiveness – i.e., rail transit in a heavily traveled, high-ridership corridor will tend to attract much more land and economic development than lower ridership in a weaker corridor.
But it’s precisely this faulty course of focusing overwhelmingly on coveted real estate and economic development possibilities, rather than crucial mobility priorities, that Austin’s political and civic leadership have taken. While private development interests obviously perceive that rail transit can bolster their real estate ventures, City of Austin planners and officials are clearly consumed by the prospect of higher property valuations and property tax revenues.
This was underscored at a 27 April 2012 meeting of the Transit Working Group (TWG) — the hand-picked “blue ribbon” circle of civic leaders then chaired by Austin’s Mayor Lee Leffingwell — that was dedicated almost totally to examining the prospects for real estate and economic development along what was then envisioned as an East Riverside-to-Mueller route for urban rail. (See video of meeting.)
Kevin Johns, director of the City’s Economic Growth and Redevelopment Services office, moderated a panel of key players in property development and development planning that extolled the potential for lucrative “return on investment” from the ripening urban rail plan. Significantly, the interaction of such development possibilities with actual mobility patterns and needs was not on their radar.
A major portion of this event included a PowerPoint presentation by Scott Polikov, principal of Gateway Planning, a development consultancy based in Ft. Worth and evidently under contract to the City of Austin. Polikov focused on several projects his firm was involved in, detailing other major players, future projects, projected valuations and tax revenues, and other aspects.

Scott Polikov of urban planning and development firm Gateway Planning gives presentation to TWG, 27 April 2012. Screenshot from COA video.
And what about the role of the University of Texas? As Lyndon Henry’s commentary UT should pay for East Campus urban rail — not Austin taxpayers points out, the UT administration has played its own role in distorting Austin’s planning process – mainly by demanding an eastside rail alignment, forsaking the high-density West Campus and major commercial activity on the Drag in favor of embellishing UT’s ongoing East Campus expansion program (and most recently, the development of a relatively small medical teaching facility just south of the main campus).
But UT’s influence is primarily political — the influence of being the proverbial “800-pound gorilla” that happens to sit on well over 40 acres of prime central Austin real estate (tax-exempt, nonetheless), and also happens to hold powerful connections to the Texas state government (and let’s not neglect to mention the UT system’s vast oil & gas holdings). Leaving UT aside, evidence is substantial that private business interests — property development interests in particular — have represented a major economic influence swaying the urban rail planning and decisionmaking of City officials.
Earlier planning for East Riverside and Mueller
For years, City planners and various public officials have repeatedly referred to the economic development potential and taxbase implications of their urban rail plans. An entire project — the City’s East Riverside Corridor Project — has focused on encouraging development and “revitalization” of the East Riverside area, historically a haven of medium to high-density, lower-cost, more affordable housing for both students and a segment of Austin’s lower and lower-middle-income workers and their families.
These development plans and policies, and their impact on East Riverside residents, were chronicled as early as 2007 by a landmark Austin American-Statesman in-depth examination. Dated 6 Aug. of that year, the story, titled “Banking on Riverside”, carried the ominous sub-ledes “Neighborhood in Transition” and “As explosive growth nears, where will longtime residents go?”
Statesman reporter Susannah Gonzales described the area as “one of the city’s largest concentrations of apartment complexes … home to thousands of immigrants and college students drawn by the lower rents and public transportation.” However, she noted, massive change was on the way. “Several plans for new development are under way in the vicinity.” Gonzales portrayed a determined effort by the City administration to expunge cheaper, affordable residential facilities and replace them with upscale condos, offices and retail outlets in a process of densification and gentrification.
Those early signals of East Riverside development, and subsequently the official corridor project, provide critical clues as to the thrust of City of Austin policy. And urban rail planning has been molded to support this policy, not just in East Riverside but in other areas deemed lucrative for both private development interests and City taxbase enhancement goals.
The Mueller development site also fits into this pattern. Since the early 2000s, the private development giant Catellus has proceeded, under City authority, to replace this former primary airport site with a 700-acre, mixed-use development envisioned to include 4,900 residences, over 650,000 square feet of retail space, and some 4.2 million square feet of office/commercial space. Until insider desires shifted in the course of the Project Connect urban rail “study” a year ago — reflecting development appetites eyeing the Highland ACC site — urban rail was planned to be routed into the Mueller project area. And Catellus has been assured that the current Red River-Hancock Center alignment will facilitate an eventual urban rail connection if the proposal on the November ballot is approved by voters. Indeed, “urban rail” planning actually began (c. 2005) as a streetcar “circulator” plan aimed at linking Mueller to UT’s East Campus and the Core Area.
Private interests that stand to gain
From a variety of reliable sources, Austin Rail Now has been able to compile a fascinating listing of many of these private property and economic development interests that stand to gain from the proposed Highland-Riverside urban rail proposal — ranging from property owners that might benefit from upward valuations to major development firms with projects already completed or under way. While some of these business interests undoubtedly have contributed to election campaigns of some councilmembers, our assessment is that City policy has been dominated by expectations of increased economic development and elevated property values, leading to expansion of taxbase and increases in property tax revenues. (The pitfalls of basing urban rail planning on such expectations have already been noted, above.) In any case, a number of these interests can be considered major players in the evolution of City urban rail planning and policy decisions. (Also see infographic at top of this post.)
► East Riverside corridor — The Statesman article of 6 August 2007 listed ten specific developer or property-holder interests with projects either planned, under construction, or completed in this area. These included:

Development interests in East Riverside area as of 2007. From Austin American-Statesman report, 2007/08/06.
The 2007 article included a map and key of the specific developments:
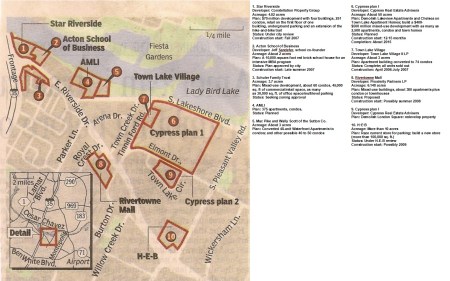
Map and key of East Riverside developments as of August 2007. Screenshot of scan of Statesman map by Dave Dobbs. (Click to enlarge.)
► South Shore — This area, also called the South Bank, just across the river (Lady Bird Lake) from Austin’s CBD, seems to be regarded as especially lucrative because of the availability of high-dollar river views for office buildings and condominiums. It was featured in Scott Polikov’s 2012 presentation to the TWG, which indicated how a new urban rail bridge across the river would benefit existing property owners, and help open up the area for a future development boom:

Slide from 2012 Gateway presentation to TWG showed adjacent South Shore property owners that stood to benefit.

Slide from 2012 Gateway presentation to TWG showed possible future South Shore development boom.
The Gateway presentation also described the possible economic payoff from South Shore development stimulated by urban rail:

Slide from 2012 Gateway presentation to TWG showed possible economic and tax benefits of urban rail plan in South Shore area.
In summary, major current beneficiaries of the proposed urban rail project through the South Shore area would include:

Development interests in South Shore area.
► Eastside CBD — This area lies generally between Congress and I-35, from the river north to the UT campus. Information on development interests has been compiled from the Downtown Austin Alliance Emerging Projects listing, the Gateway 2012 TWG presentation, and a knowledgeable political consultant speaking on background. According to this last source, several major developers and speculators are acquiring large property holdings (entire blocks in some cases) along and near the East 6th St. area in anticipation of the valuation effects of urban rail as well as the Waller Creek project.
Based on these sources, some major beneficiaries of the proposed urban rail project through the east side of the CBD include:

Development interests in east side of CBD.
The Gateway 2012 TWG presentation also zeroed in on a possible development boom, bolstered by the proposed urban rail alignment, engulfing the Rainey St. neighborhood, in the southeast corner of the CBD:
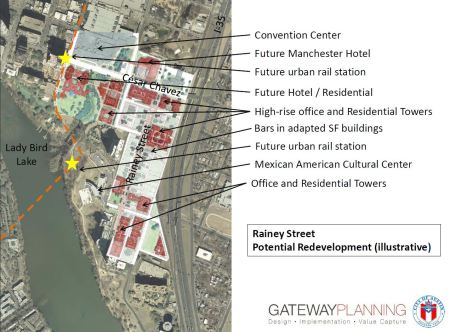
Slide from 2012 Gateway presentation to TWG showed possible future Rainey St. development boom.
Hypothetical economic benefits were also listed:

Slide from 2012 Gateway presentation to TWG showed possible economic and tax benefits of urban rail plan in Rainey St. neighborhood.
► Airport Blvd. corridor and Highland ACC area — Information on development interests in these segments of the City’s proposed urban rail route has been derived from a 28 Aug. 2011 article in the Austin American-Statesman, the 2012 TWG presentation by Gateway Planning (which has been involved in recommending and projecting economic and real estate development for the Airport Blvd. corridor), and a 2 Nov. 2012 article from the Austin Business Journal.
Reportedly, planners and officials envision a “new urbanist” redevelopment with classroom facilities, administrative offices, “and a mix of residential, retail and other commercial development.” (Statesman) The RedLeaf development is aimed to be “a thriving public-private complex with perhaps 1,250 residential units”. Major private development players cited in these sources include:

Development interests in Highland ACC and Airport Blvd. area.
Along and east of the Highland site, the Airport Blvd. corridor is proposed for a massive overhaul. Giving some visualization of what the character of development along this corridor could look like, the Gateway 2012 TWG presentation provides a slide showing a proposed transit-oriented development (TOD) project in the Fiskville neighborhood along the corridor:

Slide from 2012 Gateway presentation to TWG showed rendering of possible TOD in Fiskville corridor near Airport Blvd.
As this post has already emphasized, there’s nothing illicit or irregular with private development interests seeking opportunities to locate new projects near rail transit stations. But in the case of the urban rail plan now proposed for bond funding via a proposition on this November’s ballot, considerations of economic and real estate development potential — and expectations of increased property valuations and tax flows for local government budgets — seem to have trumped essential mobility priorities and thoroughly distorted the planning process and the proposed rail plan.
Likewise, it should be noted that there’s no assumption that interests listed in this post that stand to benefit from the routing of urban rail have directly intervened to influence urban rail planning. However, it is known that some real estate and development interests have been listed as contributors to the semi-official Let’s Go Austin campaign leading the effort to advocate passage of the bond funding measure. ■