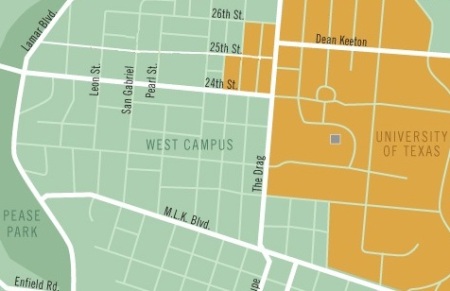
Project Connect map (annotated by ARN) showing half-mile radius from proposed urban rail stations. Except for a mainly commercial and retail sliver along the Drag, most of high-density West Campus residential neighborhood is beyond station access radius.
♦
By Lyndon Henry
The following comments were made during Citizen Communications to Project Comnnect’s Central Corridor Advisory Group (CCAG) on 13 June 2014 regarding Project Connect’s proposed 9.5-mile, $1.4 billion urban rail starter line connecting East Riverside (southeast) with the Highland ACC site now under development (north). Ultimately, the group voted to recommend Project Connect’s proposal to the City Council.
Since 2006, UT has insisted on a San Jacinto route that would bolster its development aims for the East Campus. However, the West Campus is where the people are, with the third-highest residential density in Texas. It’s where the heavy travel flow is, and where most activity is clustered. And the FTA-required half-mile demographic “watershed” around proposed urban rail stations on San Jacinto barely touches the eastern edge of the West Campus. (See map at top of this post.)
Meanwhile, although insisting that its East Campus development program must be served by Austin’s urban rail, the UT administration has not offered a dime to fund it. Instead, they’ve happily assumed that Austin taxpayers can obligingly be squeezed with higher property taxes to pay for this amenity.
There’s a “reverse-Robin-Hood” aspect to this. Because of shale oil extraction on Permanent University Fund lands, according to a San Antonio Express-News report last year, “The University of Texas System is rich. … Oil is the reason why.”
The UT system is awash in money to the tune of a billion dollars a year, boosting UT Austin’s share to a total of nearly $200 million. Profits from football and other athletic entertainment bring in another $78 million a year.
While there are certainly various needs for this money — particularly the need to keep tuition costs affordable — and some constraints on how it’s used, it would seem logical and fair that, if UT desperately wants urban rail in the relatively less dense, less active San Jacinto route, UT should dip into its own resources to pay for it.
An East Campus-Medical School alignment could be installed as a branch from the Guadalupe-Lamar alignment proposed as an alternative to Project Connect’s plan. UT could cover the $45 million local cost in five years by modest annual dollops of $9 million from its abundant revenues.
This compromise alternative could buttress the feasibility of urban rail and increase the benefit to the entire Austin community. But UT’s administration needs to stop trying to soak Austin taxpayers, and take responsibility for funding its fair share of what it wants.