Project Connect slide illustrating “Autonomous Rapid Transit” technology at joint Capital Metro/City of Austin work session Sep. 14th represents currently hypothetical, undeveloped technology as question mark, yet proposes it for inclusion in new “Vision Plan”. Meanwhile, plan with proven, available modes including light rail transit (LRT), presented in February 2018, has been withdrawn. Graphic: Project Connect.
♦
by Lyndon Henry
This post is a publication of comments made by Lyndon Henry to a public hearing held by the board of directors of Capital Metropolitan Transportation Authority on 17 September 2018. (The remarks refer to a “presentation this past Friday” – made by Capital Metro’s Project Connect planning team to a Joint Capital Metro Board/City of Austin City Council Work Session on Friday 14 September.) Henry is a technical consultant to the Light Rail Now Project and a contributing editor to the Austin Rail Now website.
I’m Lyndon Henry, a transportation planning consultant, former Capital Metro Board member, and currently a writer for Railway Age magazine.
Seven months ago, Project Connect at last presented a viable, attractive public transport plan, centered on a central light rail line from Tech Ridge to Slaughter Lane that would connect the city’s heaviest local travel corridors – Lamar-Guadalupe and South Congress. It was a plan that won substantial acclaim from the community and reflected what was already supported in public surveys.
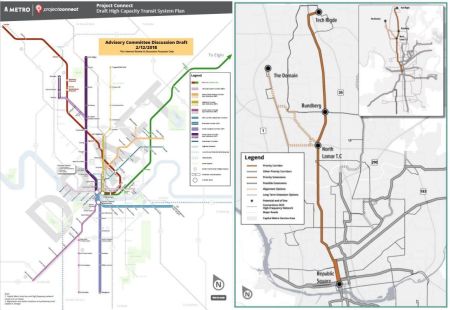
Left: Project Connect draft system plan (presented in Feb. 2018) proposed multiple bus and rail routes, including long north-south light rail line (shown in purple north of the river and lavender to the south) stretching from Tech Ridge to Slaughter Lane. Right: Initial phase of LRT project (proposed Feb. 2018) would run from Tech Ridge to downtown at Republic Square, mainly following the North Lamar-Guadalupe corridor. Maps: Project Connect. (Click to enlarge.)
Astoundingly, within a month that plan was taken off the table, and apparently discarded. To judge from the presentation this past Friday, that realistic, workable plan has now been replaced by a question mark – literally. While Austin is facing a painful and mounting mobility crisis, we’re now informed that official planning is expunging rail from consideration, and has been re-focused on a buses-only operation predicated on visions of a totally untested, effectively imaginary technology (identified with a question mark in presentation slides).
This recent abrupt about-face in the direction of Austin’s public transport planning is extremely bad news – for urban public transport and the future mobility and livability of this entire metro area. Besides the trashing of the orderly planning process, the implications for Austin’s public transport are potentially far more seriously damaging.
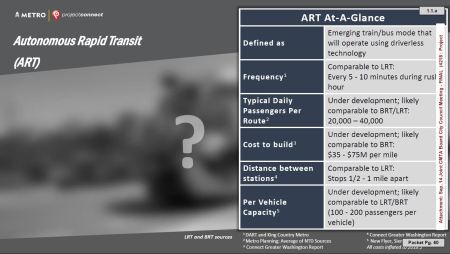
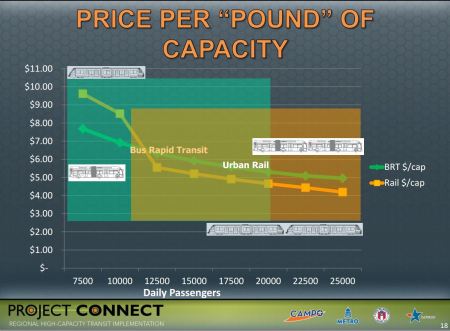
Slide from Feb. 14th Project Connect presentation shows hypothetical “Autonomous Rapid Transit (ART)” as question mark. Since mode is currently imaginary, characteristics and performance claims for it in chart are apparently based on pure speculation. Does a currently fictional technology merit inclusion in a presentation of critical public transport options? Graphic: Project Connect.
It says a lot that, since the late 1970s, at least 19 North American cities have opened brand-new light rail systems, almost every one of which has decisively reversed previously declining ridership, increased public attraction to transit, improved urban livability, sparked economic development, and attracted real estate development to cluster near the rail stations. In contrast, the results for the handful of new BRT [bus rapid transit] and quasi-BRT operations have been spotty, and at best a pale shadow of light rail’s success.
In Austin, over the past 28 years, at least three multimillion-dollar publicly sponsored comparative studies have selected light rail as the superior mode to BRT, particularly in key features such as capacity, cost, and various community impacts.
While new technology can improve transit, it must be rigorously tested and proven. But in terms of demonstrated workability and performance, the latest “transit vision” of “a regional system of autonomous, electric-powered buses moving in platoons” is little more than a fantasy, and quite possibly a fraud. Four years ago, the Project Connect team rejected reliance on “Newer technology that does not have proven application”, and warned that “Unproven technologies have unforeseen costs”. Now those caveats have disappeared, replaced by assurances and hype.

Project Connect chart from 2014 includes warnings (annotated with red arrow) against “Unproven technologies”. Graphic: Project Connect.
But what proponents seem to be actually committing Austin to, in reality, is BRT for the region’s major “high-capacity” transit system. The idea seems to be to place all our hopes on an unproven hypothetical technology that will emerge – and be satisfied with BRT in the meantime.
Yet while the Austin region’s mobility crisis continues to worsen as I speak, light rail is available now, a well-proven mode with a long record of success. It’s out-performed BRT and proven far more affordable than subway-elevated alternatives. I urge you to reinstate that February plan with a central light rail spine so Austin can continue to move forward with a real-world solution to our mobility crisis.
Thank you for the opportunity to put these observations and warnings in the public record.
■