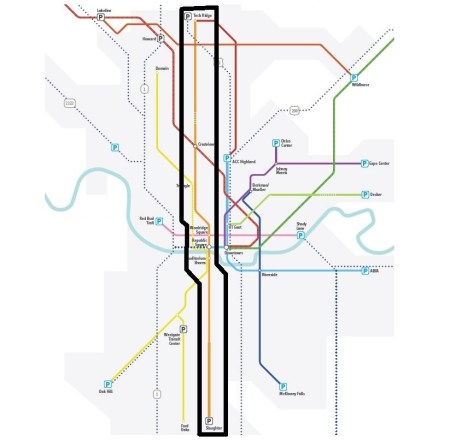
Orange Line (north-south route indicated within black outline) shown within Project Connect’s map of proposed regional system. Excerpted and edited by ARN.
By Austin Rail Now
Commentary originally produced by ARN and distributed (as one-page handout) to participants in Project Connect’s Orange Line Workshop at Austin Central Library, 17 July 2019.
♦ Light rail transit (LRT) — This well-proven, widely deployed, effective, affordable urban rail alternative has been proposed for the Orange Line (N. Lamar-Guadalupe-S. Congress) corridor for 30 years. Since selected as Capital Metro’s Locally Preferred Alternative in 1989, LRT has remained Austin’s premier major high-capacity transit vision. In early 2018, Project Connect 2’s proposal for LRT in the Orange Line corridor received widespread community acclaim. However, the proposal was subsequently quashed by Capital Metro, which proceeded to restart the Project Connect process.
As noted below, LRT has demonstrated numerous key advantages over bus rapid transit (BRT). And unlike many “gadget” alternatives, LRT is well-proven in public service, a readily available technology, and non-proprietary. (In contrast, “autonomous BRT” has been neither deployed commercially nor even tested.)
♦ Ridership — On average, light rail systems have excelled in attracting passengers, especially new riders who have access to a car but choose to ride LRT. Compared with buses, LRT systems are more user-friendly, more comfortable to access and ride, and perceived as safer and more reliable. On average, ridership on new LRT systems is 127% higher than on bus rapid transit (BRT).
http://www.lightrailnow.org/industry_issues.htm#ridership • http://www.lightrailnow.org/industry_issues.htm#mode-preference
APTA/NTD
♦ Affordability — Especially for a city of Austin’s size, light rail has typically provided an affordable capital cost opportunity to install urban rail (costs similar to “real” BRT), with significantly lower operating + maintenance cost per passenger-mile compared to buses. Average operating cost of new LRT systems is 10% lower than for BRT. The lower capital and operational costs of a predominantly surface LRT system make it the ideal affordable mode for future expansion of a rail transit network throughout the Austin metro area.
http://www.vtpi.org/bus_rail.pdf • National Transit Database
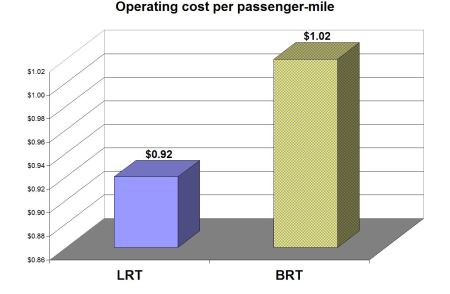
Average operational cost of LRT is 10% lower than for BRT. Average costs calculated by ARN from data reported to National Transit Database, 2016.
♦ Environment & energy — Evidence shows LRT systems have the lowest air pollution and noise impacts, preserve neighborhoods and urban quality of life, and reduce energy usage per passenger-mile compared with cars and buses. LRT especially avoids the energy-wasting effects of hysteresis and asbestos pollution of rubber-tire transport.
http://www.lightrailnow.org/industry_issues.htm#environmental-impacts • http://onlinepubs.trb.org/onlinepubs/circulars/ec145.pdf
♦ Urban benefits — In contrast to bus operations (including BRT), light rail systems have demonstrated a consistent, significant, superlative propensity to attract adjacent development and economic growth, and help shape and guide a changing urban landscape.
http://www.lightrailnow.org/industry_issues.htm#urban • http://onlinepubs.trb.org/onlinepubs/Conferences/2019/LRT/LyndonHenry.pdf
♦ Capacity — Compared to both buses and “gadget” modes, LRT has far higher capacity in normal service scenarios and greater capability to accommodate future demand.
https://www.thoughtco.com/passenger-capacity-of-transit-2798765
♦ Guadalupe-Lamar (G-L) corridor — Positioned as Austin’s major central local corridor, between I-35 to the east and Loop 1 (MoPac) to the west, G-L has repeatedly been regarded as ideal for an LRT surface starter line (with no need for major civil works) to create the key central spine for an eventually citywide and regional urban rail network. It’s the center city’s 3rd-heaviest north-south corridor. The City of Austin (COA) has repeatedly emphasized that G-L is the primary local traffic corridor in central-city Austin, with exceptionally heavy traffic at maximum capacity for over the past 2 decades. Texas Transportation Institute ranks North Lamar as one of the most congested arterials in Texas. Urban rail is essential to maintaining mobility in this crucial corridor.
https://austinrailnow.com/2014/10/13/latest-tti-data-confirm-guadalupe-lamar-is-central-local-arterial-corridor-with-heaviest-travel/
♦ Employment & population density — With Austin’s highest total employment density on Guadalupe-Lamar, an urban rail line could serve 31% of all Austin jobs. An urban rail line in this corridor would serve the highest-density residential concentrations in the city — including the West Campus, ranking as the 3rd-highest in residential neighborhood density among major Texas cities.
http://centralaustincdc.org/transportation/austin_urban_rail.htm

